

How an artificial intelligence-based classification algorithm assigns a category, such as ‘diseased’ or ‘healthy’, to a radiological image, is typically not intelligible for the user. The therefore predominantly used neuronal networks behave like a black box – the learned image features guiding the networks decision remain elusive for the user.
For years, VRVis has been dedicated to researching AI solutions that are not only explainable and intuitive, but also reliable, producing comprehensible and trustworthy decisions. To achieve this goal, we are developing methods that make the neural network's decision-making process transparent to the user. These methods not only give medical professionals additional feedback on the reliability of the decision but also help developers in verifying the quality of the trained network.
Publications
D. Major , D. Lenis , M. Wimmer , A. Berg , T. Neubauer , K. Bühler (2023): On the importance of domain awareness in classifier interpretations in medical imaging. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging
Videos
Media reports
"Sicherheit in der Unsicherheit – Zuverlässige KI in einer komplexen Welt", in: APA Science (2024)
"XAI – Vertrauenswürdige Künstliche Intelligenz: Das Denken der Neuronalen Netze verstehen lernen", in: APA Science (11/2022)
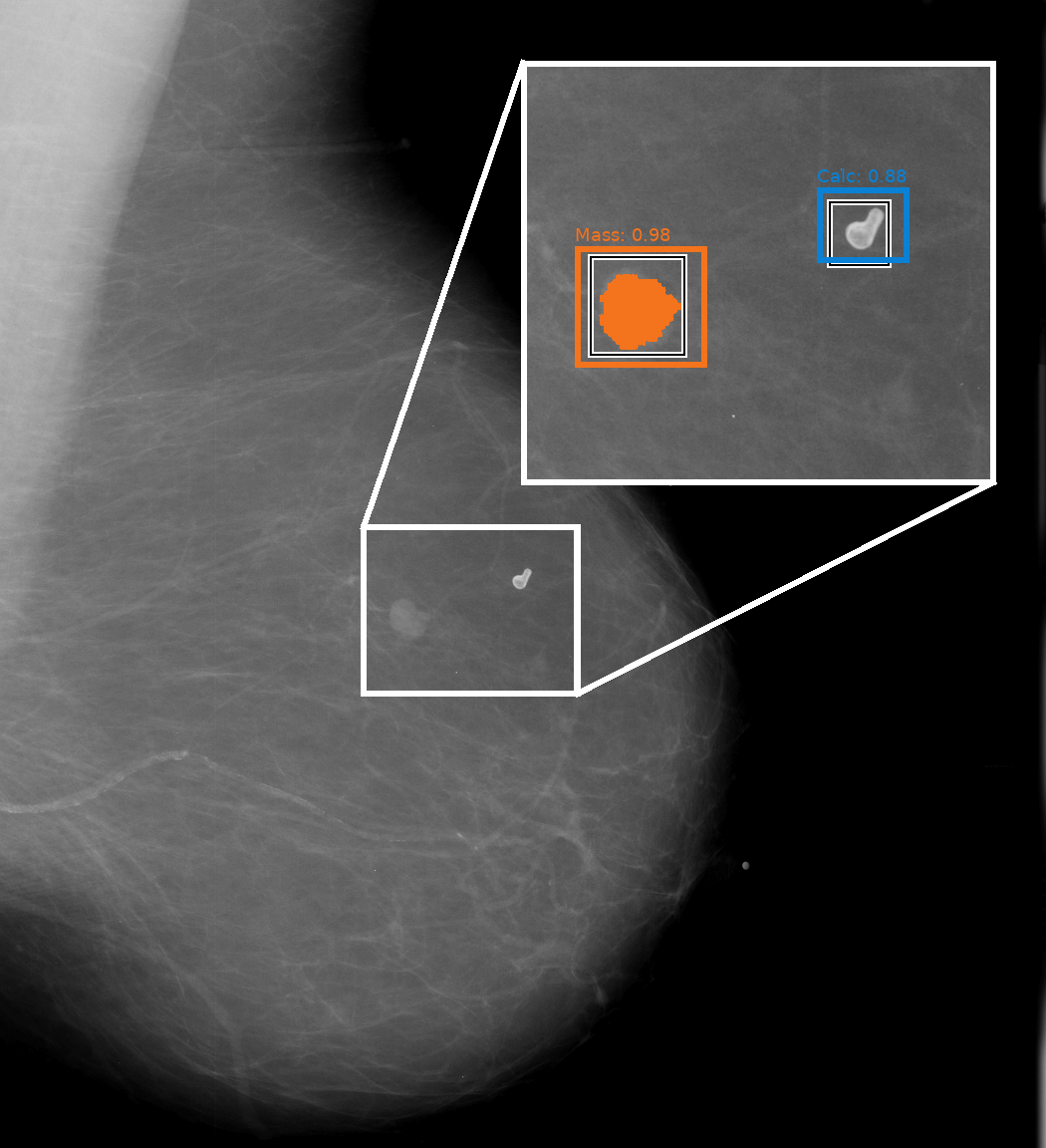
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women worldwide. Thus, the exact analysis of mammography images is an important task in radiology, since the early detection of risk factors and possible suspicious regions in the breast is crucial for successful therapy.
In cooperation with our long-term partner Agfa HealthCare, we developed various deep learning approaches for the analysis of mammography data. We combine several deep learning models that are focused to specific medical questions, such as where pathological lesions and microcalcifications are located in an image or whether a patient has denser breast tissue. This allows us to improve patient-level predictions based on the specific results of the individual models. The modular design of our solution and the possibility to access task specific decisions individually is increasing the explainability of the model and trust in its overall decision. To further increase trust in individual black box deep learning models and their decisions, we developed several novel approaches for explaining AI decisions in the context of image-based decision making.
Publications
Videos

The exact segmentation of soft tissue tumors in multimodal data is of high importance in various medical domains, e.g. for surgery and biopsy planning or in radiotherapy. For this purpose multimodal data like MRI and PET/CT data is acquired, whereby the tumor segmentation may look different, depending on the modality and clinical task
In cooperation with the Medical University of Vienna, we developed and compared different methods to segment soft tissue tumors. We focused specifically on the modality- and task-specific soft tissue tumor segmentation, and how we can fuse multimodal data efficiently to improve the quality of the segmentation.
Publications
Videos
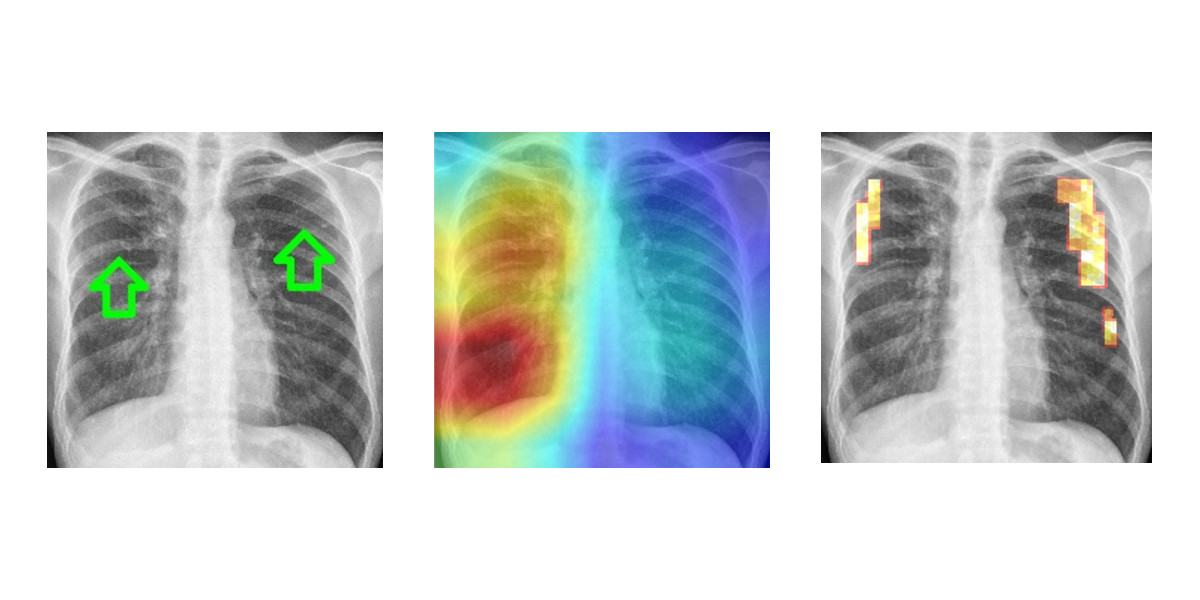
In order to support medical professionals in patient screening to detect tuberculosis infections, VRVis has developed a deep learning-based application in collaboration with Agfa Healthcare. With large numbers of patients, it assists in identifying diseased individuals more rapidly, optimising further diagnosis and treatment courses. Find more information in our press release.
![Medical Image Registration [Translate to English:] Zu sehen sind zwei Spalten an medizinischen Röntgenbildern des Brustbereichs, daneben sind zwei Spalten von medizinischer Bildregistrierung derselben Aufnahmen.](/fileadmin/01_Forschung/00_Forschungsgruppen/Biomedical_Image_Informatics/pathologies_highres_Querformat3_01.jpg)
Medical image registration is an integral part of medical analysis workflows. It allows different images of one or more patients to be analyzed in a directly comparable way by transforming the images into the same coordinate system. Registration is necessary to compare images between studies acquired at different time points or between different modalities.
VRVis has developed methods for classical and deep learning based image registration in collaboration with its medical partners, and in particular investigated how visualization can support registration workflows and highlight problems.
Publications
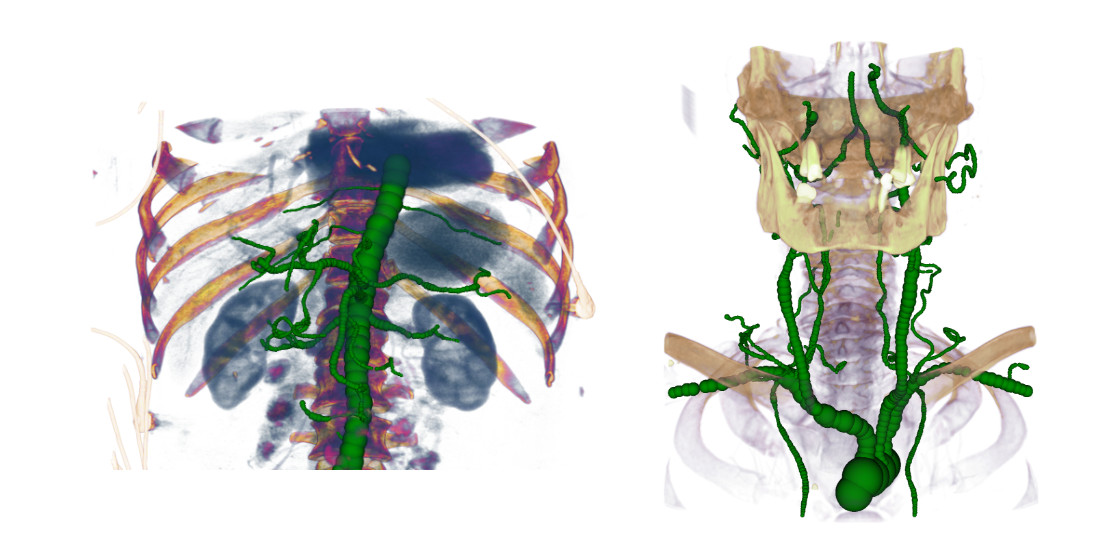
According to the World Health Organization, arteriosclerosis ist the no.1 cause of death globally. A detailed analysis of blood vessels in 3D angiograms is generally very time-consuming. In collaboration with Agfa Healthcare, VRVis has developed several methods for efficient semi-automated and fully automated segmentation of peripheral and coronary blood vessels, as well as their semantic annotation; some of these methods have won awards, been published in high-impact journals, patented and integrated into our customers’ products.
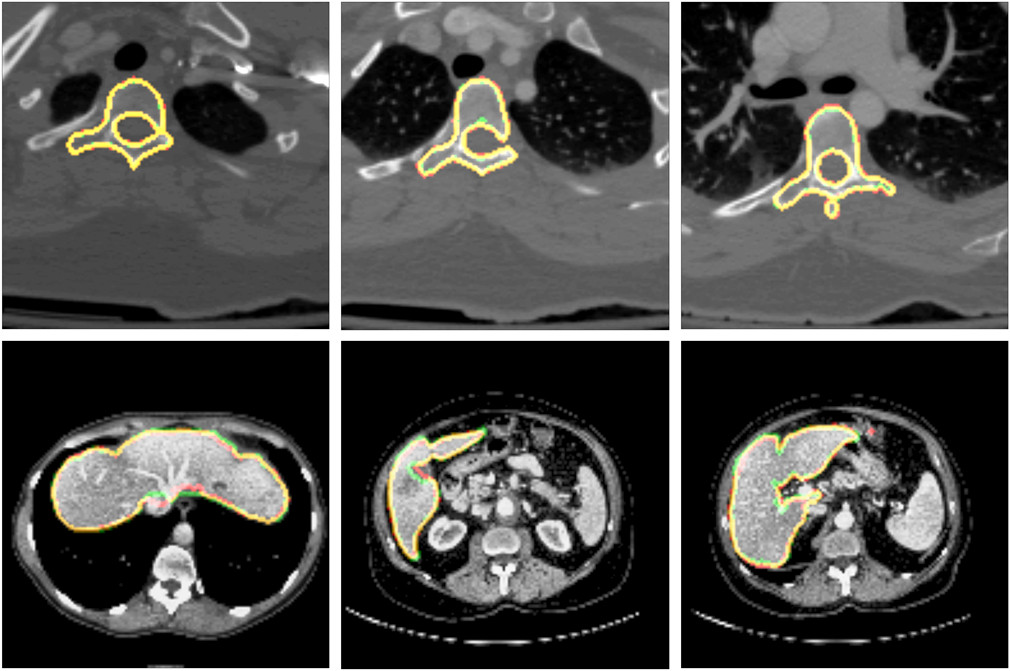
VRVis has developed and patented a number of basic methods for medical image analysis. These include widely cited AI methods for simultaneous segmentation of several objects on radiology images, sequential segmentation methods for CT image data, efficient feature detection methods, as well as several basic methods for statistical shape and texture models which, for example, are still used in combination with AI methods for difficult tasks in organ segmentation.
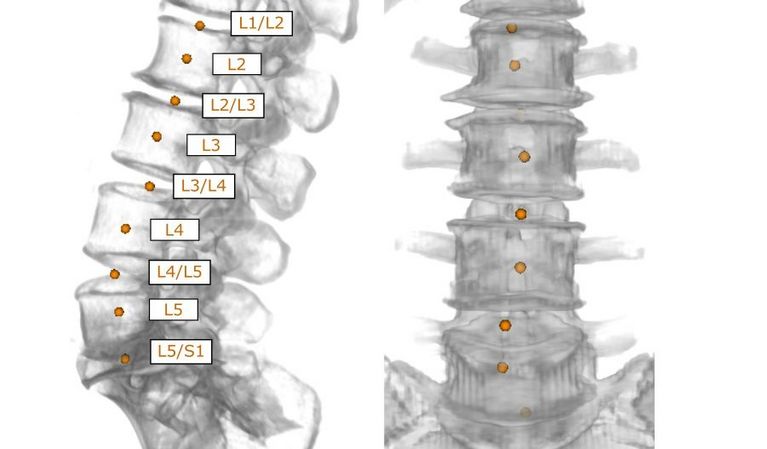
The spine is an important reference system in the human body for describing the site of pathologies during a radiological examination. For this reason, the anatomical name of each visible vertebra in the image must be known and, in many countries, has to be labelled on the image by radiologists manually. This time-consuming work has to be performed by radiologists in addition to the actual diagnosis within a short space of time. VRVis has developed a group of algorithms which can fully automatically recognise and correctly annotate the anatomy of the human vertebrae from different MR and CT scans independent of the image section. This important automated preparatory work simplifies the radiologist’s work and provides more time for the actual diagnosis.

Today, cardiovascular diseases are the most common cause of death in Austria. A detailed analysis of (time-dependent) 3D image data of the beating heart and coronary arteries in a patient is extremely time-consuming. Fully automated methods which simplify the quantification of heart pathologies can therefore make a considerable contribution to accelerating the diagnosis by the radiologist. VRVis has already developed several solutions for segmenting the heart ventricles on CT and MR images as well as an award-winning solution for fully automated segmentation of coronary arteries.

In association with our application-oriented research work for our business partner Agfa Healthcare, many patents for AI-based solutions have been produced in our in-house basic research, for example on the fully automated segmentation and annotation of blood vessels or human vertebrae. You can find out more about our patents.
The long-term vision of this applied research project is to use available data resources to improve image-based diagnostics based on complex data in daily clinical routine.
The strategic project forms the organizational and scientific hub for the realization of an area wide integrative visual computing approach. It covers joint strategic research and development on fundamental challenges in all application projects.

VRVis a founding member of the Austrian BioImaging/CMI, which is a professional consortium of multiple Austrian science institutions and the official Austrian Euro-BioImaging initiative.
COMULIS is an EU-funded COST Action that aims at fueling collaborations in the field of correlated multimodal imaging (CMI).
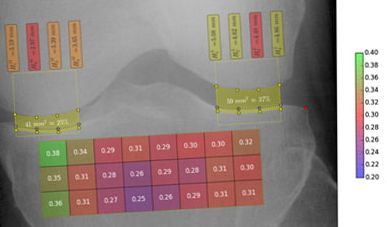
Visual computing techniques for the automated detection of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.
Visual computing for medicine: image processing solutions for new applications in radiology.
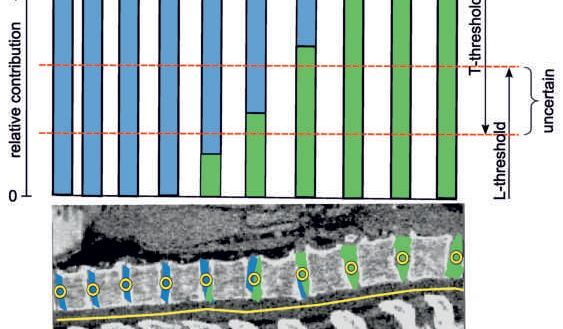
The analysis, visualization and exploration of high-dimensional image spaces are the subject of the KAFus project.

Next generation workflows for interactive knowledge generation from images and simulations.

Software for the use of multi-modality images in external radiotherapy.

On March 3, 2020, Katja Bühler, head of our Biomedical Image Informatics Group, was awarded with the renowned TU Women's Prize.

Visual computing for computer-aided diagnostics and operation planning.

Sebastian Zambal, Jiří Hladůvka, Armin Kanitsar, Katja Bühler, Shape and Appearance Models for Automatic Coronary Artery Tracking, WON MICCAI 2008 Contest: 3D Segmentation in Clinic: A Grand Challange.

C. Langer, M. Hadwiger, K. Bühler, Interaktive diffusionsbasierte Segmentierung von Volumendaten auf Grafikhardware, Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2005; GI Informatik Aktuell; Springer Verlag. pp 168-17, BVM 2005 Best Poster