
Remote Sensing
REMOTE SENSING pertains to information about places or objects that are physically difficult to access. Scenarios include rock walls or building facades photographed by drone flight, and continents or distant planets reconstructed from satellite data. We create solutions adapting remote sensing methods to different requirements. Our research results range from interactive visualization of the surface of Mars for planetary research/space travel, to the generation of BIM models from scans of existing structures. The innovative bridging between data acquisition and semantic modelling is important to us.
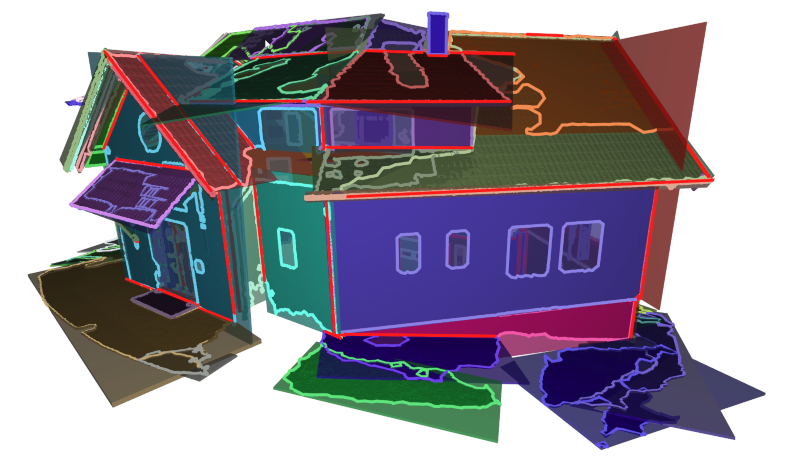
Semantic reconstruction
REMOTE SENSING pertains to information about places or objects that are physically difficult to access. Scenarios include rock walls or building facades photographed by drone flight, and continents or distant planets reconstructed from satellite data. We create solutions adapting remote sensing methods to different requirements. Our research results range from interactive visualization of the surface of Mars for planetary research/space travel, to the generation of BIM models from scans of existing structures. The innovative bridging between data acquisition and semantic modelling is important to us.
Inklusive digitization
In order to make the museums of the future barrier-free, we have been conducting intensive research for many years in the field of INCLUSIVE DIGITIZATION to find IT-based solutions that can make the fine arts "visible" to all target groups. To this end, we have developed, among other things, special visualization software that creates a digital 2.5D model from 3D scans or photographs of museum objects. Using an innovative milling process, this model can be transformed into a tactile relief that makes heights, depths, surface structures, etc. haptically perceptible - thus equipping museums for the 21st century.
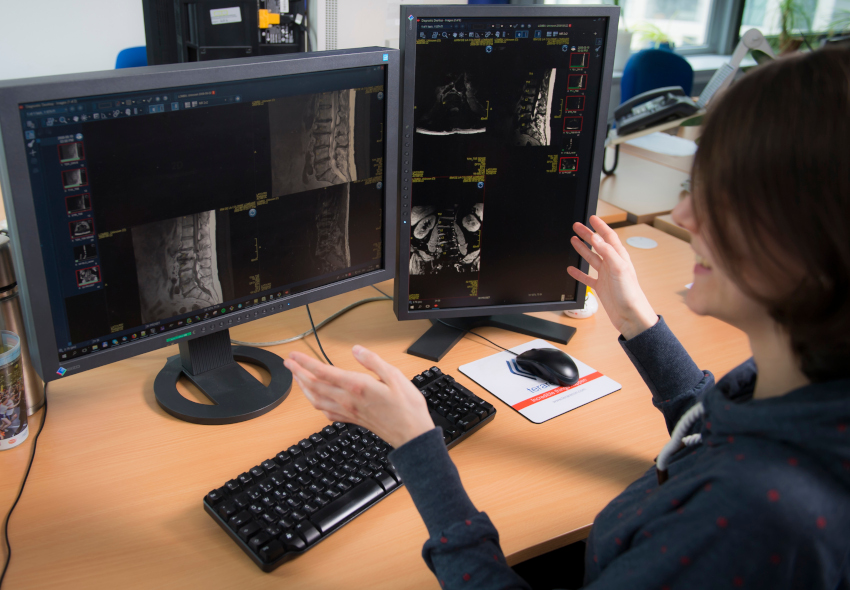
Reconstruction in medicine
For the efficient further use and ANALYSIS OF DATA OBTAINED BY IMAGING METHODS in the medical sector, we are researching innovative ways of automatically segmenting specific image content such as vertebrae, tumors or organs using machine learning and specially developed algorithms. This is an important supporting measure in the diagnostic process and also serves as a basis for reconstructions of volume data, for example.
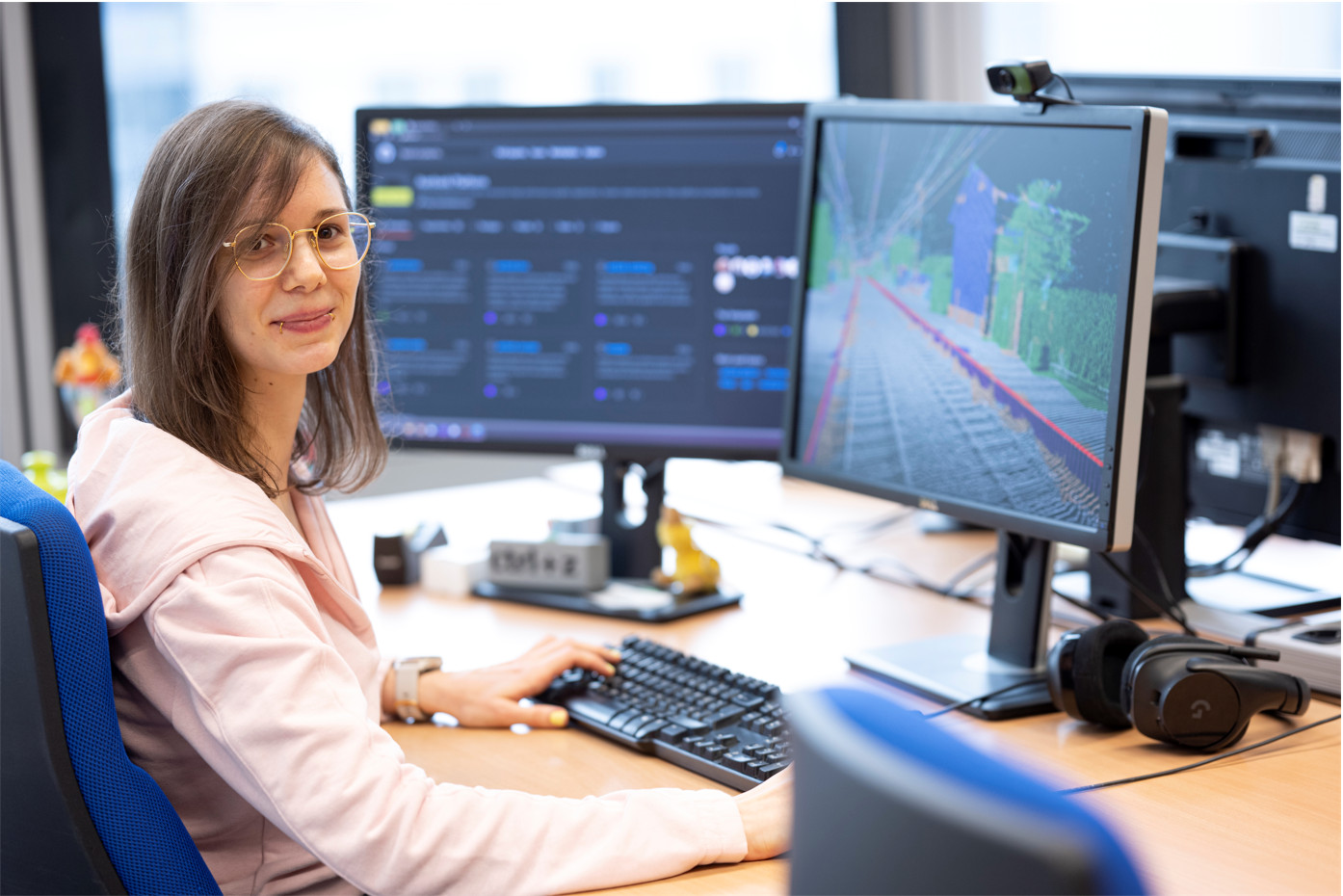

Photogrammetry
We maintain a high precision, large-scale PHOTOGRAMMETRY pipeline to enrich image-based tools and workflows. Purpose-built for terrain reconstruction from drone flights, our state-of-the-art algorithms find application in a range of use cases. We augment laser scans with precisely registered detail photos, use photo stitching to generate high-resolution orthophotos, and provide comparison views of a reconstructed area over time. Our modular and reusable implementation meshes well with upcoming innovations in low-cost scanning and AI-assisted reconstruction.
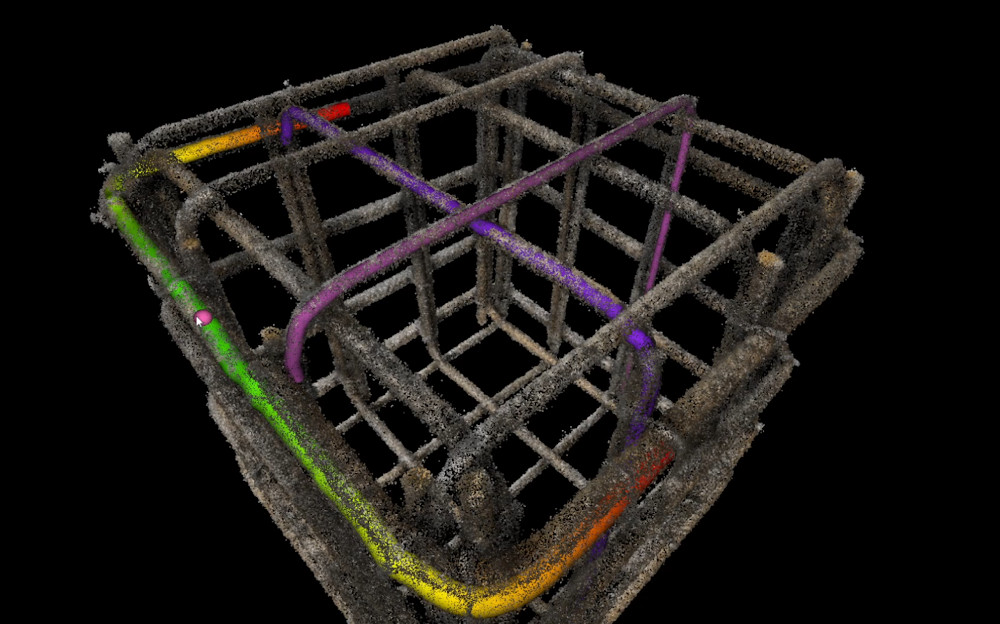
NeRFs
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) are a recent AI method for creating novel views from a set of images of an object. Since they could be used as basis for semantic reconstruction, we conducted a series of experiments. We evaluated the reconstruction results of different capturing procedures, image sizes, lighting conditions and the influence of tracking errors. We will further explore various state-of-the-art methods and develop extensions that address specific problems of our use cases.

Understanding of engineering drawings
Engineering drawings (ED) hold valuable information for a number of use cases in manufacturing. Our goal is the development of a fully automated pipeline for ED understanding and entity extraction since our partners need to process large quantities of digitized EDs to analyze the additive manufacturing (AM) potential of the represented parts. We employ image-based AI methods to extract entities including object boundaries, text fields, and dimensions, and perform guided optical character recognition (OCR) to find important textual information like materials, scales, or numeric values. The logical combination of these steps allows us to reconstruct the necessary information from EDs to analyze the AM potential of the respective parts in an interpretable way.

Construction sites are highly dynamic places, which makes complete and convenient documentation all the more important. As part of the "AI5production" program, VRVis and rmDATA are investigating whether mobile devices with LiDAR and high-resolution cameras are suitable for automatically recording construction processes in 3D.

Digitization of construction sites: VRVis and clone:it automate rebar inspection and documentation.

In construction projects, 2D plans, 3D plans, reconstructions or real world data run in parallel without being linked to each other. VRVis and PlanRadar are now bridging this gap with a mobile AR tracking solution, the Onsite-AR project.

With the help of 3D printing (additive manufacturing), spare parts for defective trains can be produced more easily and in a sustainable way as well as faster and cheaper - a great potential for the climate-friendly future of train transport companies.

The research goal of AMASE is to create a suite of tools and methods to ingest, process, visualize, and manipulate heterogeneous, large-scale geospatial data. This data is the constantly updated representation of the real world in the form of an evolving digital twin.

The main objective of the strategic project ARCS is the design of software architectures that enable interactive visualization systems to ingest large volumes and velocities of geospatial and associated non-geometric data.

Together with Rhomberg Bau GmbH and convex ZT GmbH, VRVis is developing a concept for the use of Boston Dynamic's robot dog "Spot" for autonomous, immersive construction site documentation.

WIBSTAC addresses the usage of wide baseline stereo 3D reconstruction for medium- and long-range mapping of the Martian surface, based on imagery from panoramic rover camera instruments.

The INDIGO research team is systematically documenting the graffiti on Vienna's Donaukanal, using these photos to create a digital twin of the walls. VRVis is currently contributing its technological expertise to the project.

No blind spots on train roofs thanks to depth cameras.

The applied research project Lightbox 2.0 focuses on the development of a photogrammetric 3D scanner for automatic and deep learning-based modeling of all kinds of keys.

In this project tools and methods for handling, administration, manipulation and evaluation of several different data sources for measurements and lighting design are developed.

Barrier-free access to art and museums for blind and visually impaired people through 3D technology.

Strategic Research in Scalable, Semantic Rendering.

Investigation of techniques enabling a seamless analysis of data from multi-run simulations on multiple degrees of detail.

Algorithms to improve the visual analysis of surface reconstructions.